If you aren’t an IT expert, the vast amount of tech terms out there can be overwhelming and hard to get your head around. We have found this to be especially true for those terms surrounding the internet and bandwidth – while you may be familiar and have heard of them, perhaps you don’t actually know what they mean and how they will impact your work.
Below is a list of commonly used terms related to the internet and bandwidth to help you burst through the jargon and get the most from your internet investment.
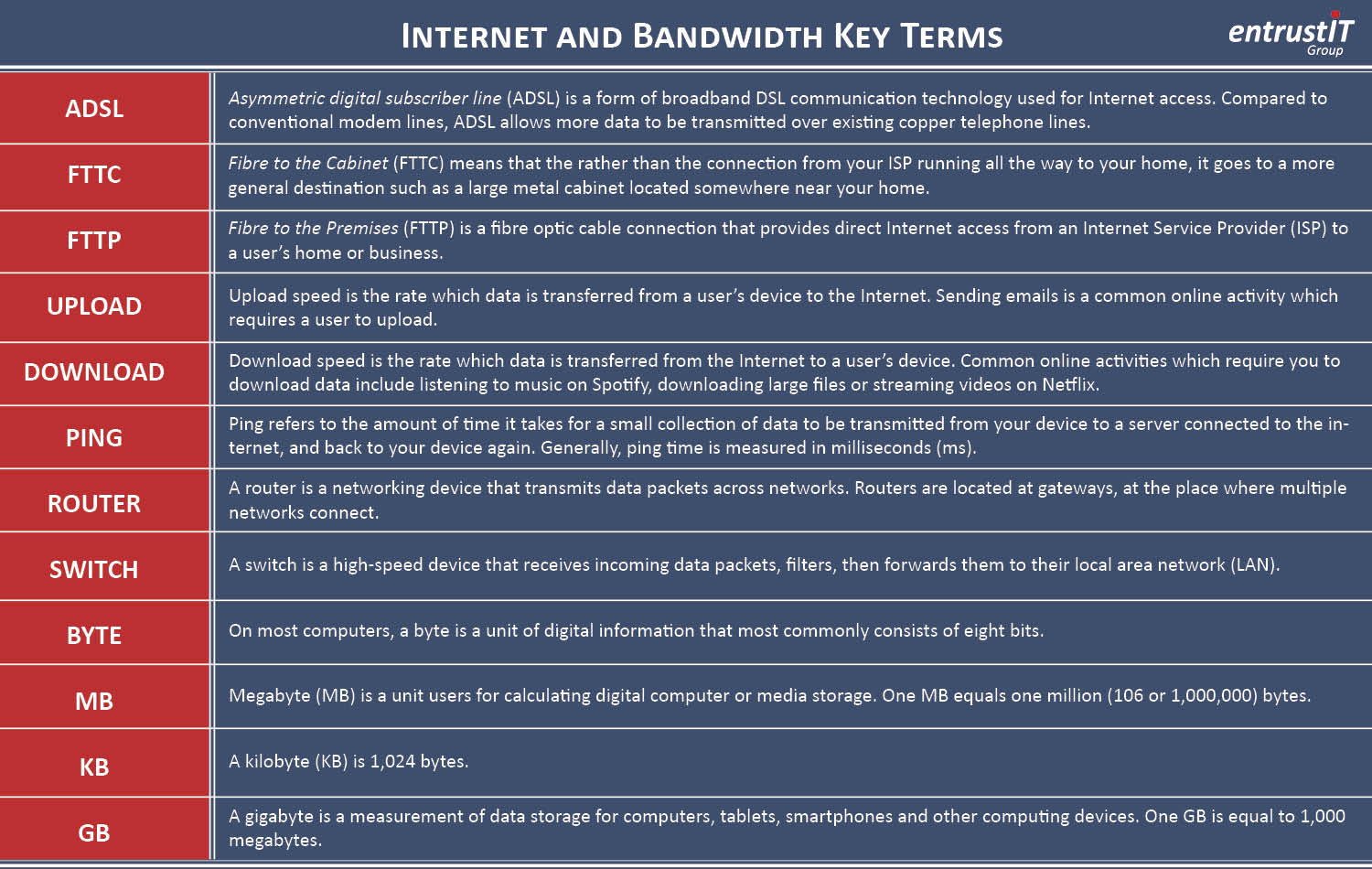
- ASDL – Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) is a form of broadband DSL communication technology used for Internet access. Compared to conventional modem lines, ADSL allows more data to be transmitted over existing copper telephone lines.
- FTTP – Fibre to the Premises (FTTP) is a fibre optic cable connection that provides direct Internet access from an Internet Service Provider (ISP) to a user’s home or business.
- FTTC – Fibre to the Cabinet (FTTC) means that the rather than the connection from your ISP running all the way to your home, it goes to a more general destination such as a large metal cabinet located somewhere near your home.
- UPLOAD – Upload speed is the rate which data is transferred from a user’s device to the Internet. Sending emails is a common online activity which requires a user to upload.
- DOWNLOAD – Download speed is the rate which data is transferred from the Internet to a user’s device. Common online activities which require you to download data include listening to music on Spotify, downloading large files or streaming videos on Netflix.
- PING – Ping refers to the amount of time it takes for a small collection of data to be transmitted from your device to a server connected to the internet, and back to your device again. Generally, ping time is measured in milliseconds (ms).
- ROUTER – A router is a networking device that transmits data packets across networks. Routers are located at gateways, at the place where multiple networks connect.
- SWITCH – A switch is a high-speed device that receives incoming data packets, filters, then forwards them to their local area network (LAN).
- Byte – On most computers, a byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits.
- MB – Megabyte (MB) is a unit users for calculating digital computer or media storage. One MB equals one million (106 or 1,000,000) bytes.
- KB – A kilobyte (KB) is 1,024 bytes.
- GB – A gigabyte is a measurement of data storage for computers, tablets, smartphones and other computing devices. One GB is equal to 1,000 megabytes.
Microsoft 365 Bandwidth Recommendations
For Microsoft 365, our bandwidth recommendations are at least 0.5Mbps upload per person. If you’re using Video Conferencing on Teams, you need 2Mbps per person.
With Citrix Hosted Workspace, you only need 128Kbps per person because it is encapsulated.
